链表 LinkedList
链表(Linked list)是一种常见的基础数据结构,是一种线性表,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个元素�由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成。
- 从数组的起点或中间插入或移除项的成本很高,由于链表不必须按顺序存储,链表在插入的时候可以达到 O(1) 的复杂度,比数组快得多,但是查找一个节点或者访问特定编号的节点则需要 O(n) 的时间,而数组相应的时间复杂度分别是 O(logn) 和 O(1)。
- 使用链表结构可以克服数组链表需要预先知道数据大小的缺点,链表结构可以充分利用计算机内存空间,实现灵活的内存动态管理。但是链表失去了数组随机读取的优点,同时链表由于增加了结点的指针域,空间开销比较大。
一列火车是由一系列车厢组成的。每节车厢都相互连接,你很容易分离一节车厢,改变它的位置、添加或移除它。每节车厢都是链表的元素,车厢间的连接就是指针。
单(向)链表
链表中最简单的一种是单向链表,它包含两个域,一个信息域和一个指针域。这个链接指向列表中的下一个节点,而最后一个节点则指向一个空值。
实现链表
LinkedList 类包含的方法:
push(element):向链表尾部添加一个新元素。insert(element, position):向链表的特定位置插入一个新元素。getElementAt(index):返回链表中特定位置的元素。如果链表中不存在这样的元素,则返回null。remove(element):从链表中移除一个元素。indexOf(element):返回元素在链表中的索引。如果链表中没有该元素则返回-1。removeAt(position):从链表的特定位置移除一个元素。isEmpty():如果链表中不包含任何元素,返回true,如果链表长度大于0则返回false。size():返回链表包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似。toString():返回表示整个链表的字符串。由于列表项使用了Node类,就需要重写继承自 JavaScript 对象默认的toString方法,让其只输出元素的值。
/**
* 判断元素是否相等
*/
function defaultEquals(a, b) {
return a === b;
}
/**
* 定义节点元素
*/
class Node {
constructor(element, next) {
// value
this.element = element;
this.next = next || null;
}
}
/**
* 定义链表类
*/
class LinkedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
// 对比函数
this.equalsFn = equalsFn;
// 用来存储链表中的 元素数量
this.count = 0;
// head 初始化为 null
this.head = null;
}
/**
* 向链表尾部添加元素
* 两种场景:链表为空,添加的是第一个 元素;链表不为空,向其追加元素
*/
push(element) {
// 实例化一个 node 节点
const node = new Node(element);
let current;
if (this.head === null) {
// 链表为空,head 元素指向 node 元素
this.head = node;
} else {
// 链表不为空,要向链表的尾部添加一个元素
// 循环访问列表,找到最后一个元素
// current 存储循环到的具体元素
current = this.head;
while (current.next !== null) {
current = current.next;
}
// 当 current.next 为 null 时,即为最后的元素
// 最后元素的 next 指针指向想要添加到链表的节点
current.next = node;
}
// 链表长度 +1
this.count++;
}
/**
* 根据 index 位置获取元素
*/
getElementAt(index) {
// 参数合法性验证
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
let node = this.head;
// 需要迭代链表的节点,直到到达目标位置
for (let i = 0; i < index && node != null; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
return node;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 在任意位置插入元素
* 两种场景:第一种场景是在链表的起点添加一个元素,第二种场景是在链表中间或尾部添加一个元素
*/
insert(element, index) {
// 合法性校验
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(element);
// 一、在第一个位置添加
if (index === 0) {
// 1. current 是链表中第一个元素的引用
const current = this.head;
// 2. 把 node.next 的 值设为 current
node.next = current;
// 3. 把 head 的引用改为 node
this.head = node;
} else {
// 二、中间或尾部添加
// 1. 迭代链表,找到目标位置
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
// 2. 新元素指针指向 previous 原来的指向地址
node.next = previous.next;
// 3. 之前元素指针指向当前添加的元素
previous.next = node;
}
// 链表长度 +1
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 按特定位置从链表中移除元素
* 两种场景:第一种是移除第一个元素,第二种是移除第一个元素之外的其他元素
*/
removeAt(index) {
// 校验参数合法性(越界值)(index 从零开始)
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
// 移除第一个元素
if (index === 0) {
// 用 head 的指向的下一个元素赋值为 head
// 这样 head 就指向列表的第二个元素
this.head = current.next;
} else {
// 移除链表的最后一个或者中间某个元素
// 1. 获取需移除元素的前一个元素
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
// 2. 取出需要移除元素节点引用
current = previous.next;
// 3. 把前一个元素的指针指向移除元素的下一个元素地址
// 丢弃移除节点在计算机内存中,等着被垃圾回收器清除
previous.next = current.next;
}
// 长度 -1
this.count--;
// 返回节点元素
return current.element;
}
return null;
}
/**
* indexOf 的方法,传入元素返回一个元素的位置
* 要比较链表中的元素是否相等,我们需要使用一个内部调用的函数,名为 equalsFn
*/
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head;
// 迭代元素,找到返回位置 i
for (let i = 0; i < this.size() && current != null; i++) {
// current 节点的元素和目标元素是否相等
if (this.equalsFn(element, current.element)) {
return i;
}
// 迭代 下一个链表节点
current = current.next;
}
// 否则返回 -1
return -1;
}
/**
* 从链表中移除元素
*/
remove(element) {
// 找到元素位置
const index = this.indexOf(element);
// 根据位置移除元素
return this.removeAt(index);
}
/**
* 链表是否为空
*/
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
/**
* 链表长度
*/
size() {
return this.count;
}
/**
* 获取链表第一个元素(head)
*/
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
/**
* 清空链表
*/
clear() {
this.head = null;
this.count = 0;
}
/**
* 获取链表值的字符串
*/
toString() {
// 链表为空,返回一个空字符串
if (this.head == null) {
return '';
}
// 循环拼接字符串
let objString = `${this.head.element}`;
let current = this.head.next;
for (let i = 1; i < this.size() && current != null; i++) {
objString = `${objString}, ${current.element}`;
current = current.next;
}
return objString;
}
}
测试
let linkedList = new LinkedList(defaultEquals);
linkedList.push('1');
linkedList.push('2');
linkedList.push('3');
// and so on ...
双(向)链表
一种更复杂的链表是“双向链表”或“双面链表”。每个节点有两个连接:一个指向前一个节点(当此“连接”为第一个“连接”时,指向空值或者空列表);而另一个指向下一个节点(当此“连接”为最后一个“连接”时,指向空值或者空列表)。
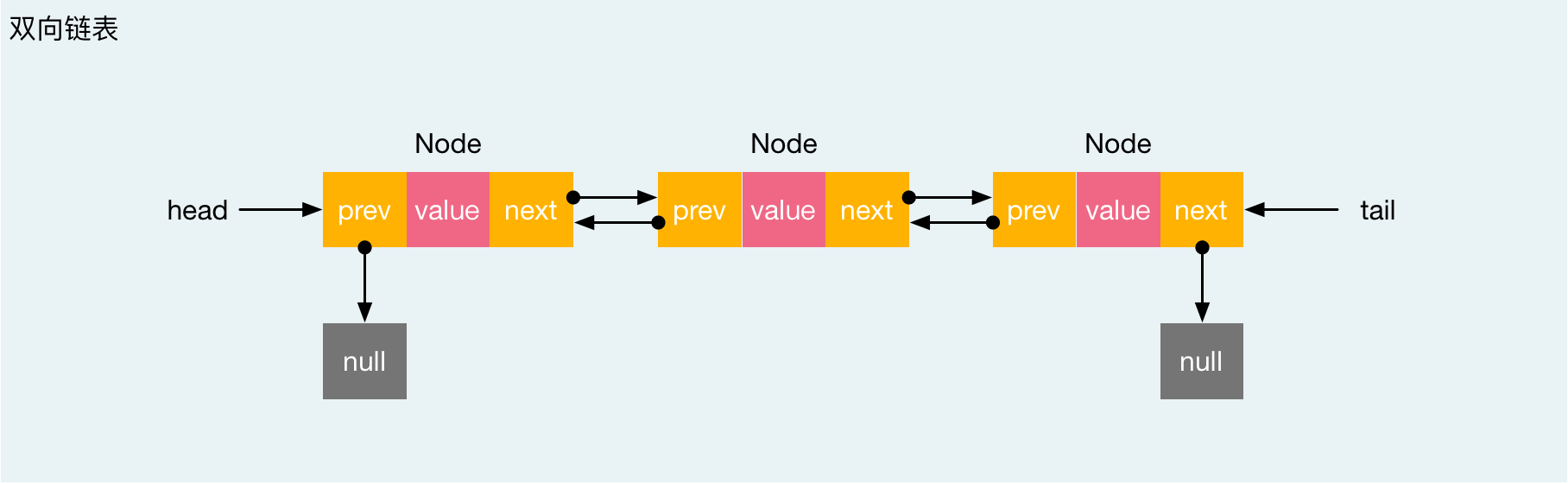
实现双链表
DoublyLinkedList (双向链表�)类是一种特殊的 LinkedList 类,我们要扩展 LinkedList (单向链表)类,重写部分方法。
// 依赖上面单链表定义的 defaultEquals
/**
* 继承前面单链表的 Node 类
*/
class DoublyNode extends Node {
constructor(element, next, prev) {
super(element, next);
// 新增前指针
this.prev = prev || null;
}
}
/**
* 继承单链表 LinkedList 类
*/
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
// 调用 LinkedList 的构造函数
super(equalsFn);
// 新增尾部,保存对链表最后一个元素的引用
this.tail = null;
}
/**
* 向双向链表添加元素
*/
push(element) {
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
// 链表为空 赋给头部和尾部
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
// 添加到尾部
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.count++;
}
/**
* 向双向链表任意位置插入一个新元素
*/
insert(element, index) {
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new DoublyNode(element);
let current = this.head;
// 场景一:在双向链表的第一个位置(起点)插入一个新元素
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == null) {
// 如果双向链表为空
// 把 head 和 tail 都指向这个新节点
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
// 如果不为空
// 1. 把 node.next 设为 current
// node.next = current;
node.next = this.head;
// 2. current.prev 指针将由指向新元素 node
this.head.prev = node;
// 3. head 指向新元素 node
this.head = node;
}
} else if (index === this.count) {
// 场景二:在双向链表最后添加一个新元素
// current 变量将引用最后一个元素
current = this.tail;
// 原最后元素 current.next 指针将指向新元素 node
current.next = node;
// 新元素 node.prev 的指针指向原最后一个元素 current
node.prev = current;
// 更新 tail 指向新最后一个元素 node
this.tail = node;
} else {
// 场景三:在双向链表中间插入一个新元素
// 迭代双向链表,直到要下标前一个元素位置
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
// 把 current 赋值为要插入下标的下一个位置元素
current = previous.next;
// 在 current 和 previous 元素之间插入新元素
// 新元素 node.next 指针将指向 current
node.next = current;
// 而 previous.next 将指向新元素 node
previous.next = node;
// 新元素的下一个元素 current.prev 指针指向新元素 node
current.prev = node;
// 而新元素 node.prev 指针将指向 previous
node.prev = previous;
}
// 双链表长度 +1
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 从任意位置移除元素
*/
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
// 场景一:从头部移除一个元素
// current 是对双向链表中第一个元素的引用,即要移除的元素。
if (index === 0) {
// 需要改变 head 的引用,将其从 current 改为下一个元素 current.next
this.head = this.head.next;
// 如果只有一项,更新 tail
if (this.count === 1) {
// 需要把 tail 也设为 null
this.tail = null;
} else {
// 把新的第一个元素 head.prev 的引用改为 null (也可以用 current.next.prev)
this.head.prev = null;
}
} else if (index === this.count - 1) {
// 场景二:从尾部移除一个元素
// 把 tail 的引用赋给 current 变量
current = this.tail;
// 把 tail 的引用更新为双向链表��中倒数第二个元素(current.prev 或者 tail.prev)
this.tail = current.prev;
// 把 next 指针更新
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
// 场景三:从中间移除一个元素
// 首先需要迭代双向链表,直到要找的位置
// current 所引用的就是要移除的元素
current = this.getElementAt(index);
// 需要移除元素 current 的前一个元素 previous
const previous = current.prev;
// 将 previous 与 current 的下一项链接起来
// previous.next 将指向 current.next
previous.next = current.next;
// current.next.prev 将指向 previous
current.next.prev = previous;
}
// 长度 -1
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return null;
}
/**
* 查找元素位置
*/
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head;
let index = 0;
while (current != null) {
if (this.equalsFn(element, current.element)) {
return index;
}
index++;
current = current.next;
}
return -1;
}
/**
* 查看头部
*/
getHead() {
return this.head;
}
/**
* 查看尾部
*/
getTail() {
return this.tail;
}
/**
* 清空
*/
clear() {
super.clear();
this.tail = null;
}
/**
* 从头部到尾部转字符串
*/
toString() {
if (this.head == null) {
return '';
}
let objString = `${this.head.element}`;
let current = this.head.next;
while (current != null) {
objString = `${objString}, ${current.element}`;
current = current.next;
}
return objString;
}
/**
* 从尾部到头部转字符串
*/
inverseToString() {
if (this.tail == null) {
return '';
}
let objString = `${this.tail.element}`;
let previous = this.tail.prev;
while (previous != null) {
objString = `${objString}, ${previous.element}`;
previous = previous.prev;
}
return objString;
}
}
可以对 insert 和 remove 这两个方法的实现做一些改进。如果 index 大于 length / 2,就最好从尾部开始迭代,而不是从头开始(这样就 能迭代双向��链表中更少的元素)。
循环链表
在一个循环链表中的首节点和末节点被连接在一起。实现方式可以像链表一样只有单向引用,也可以像双向链表一样有双向引用。
循环链表和链表之间唯一的区别在于,最后一个元素指向下一个元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用 null,而是指向第一个元素(head)。
双向循环链表有指向 head 元素的 tail.next 和指向 tail 元素的 head.prev。
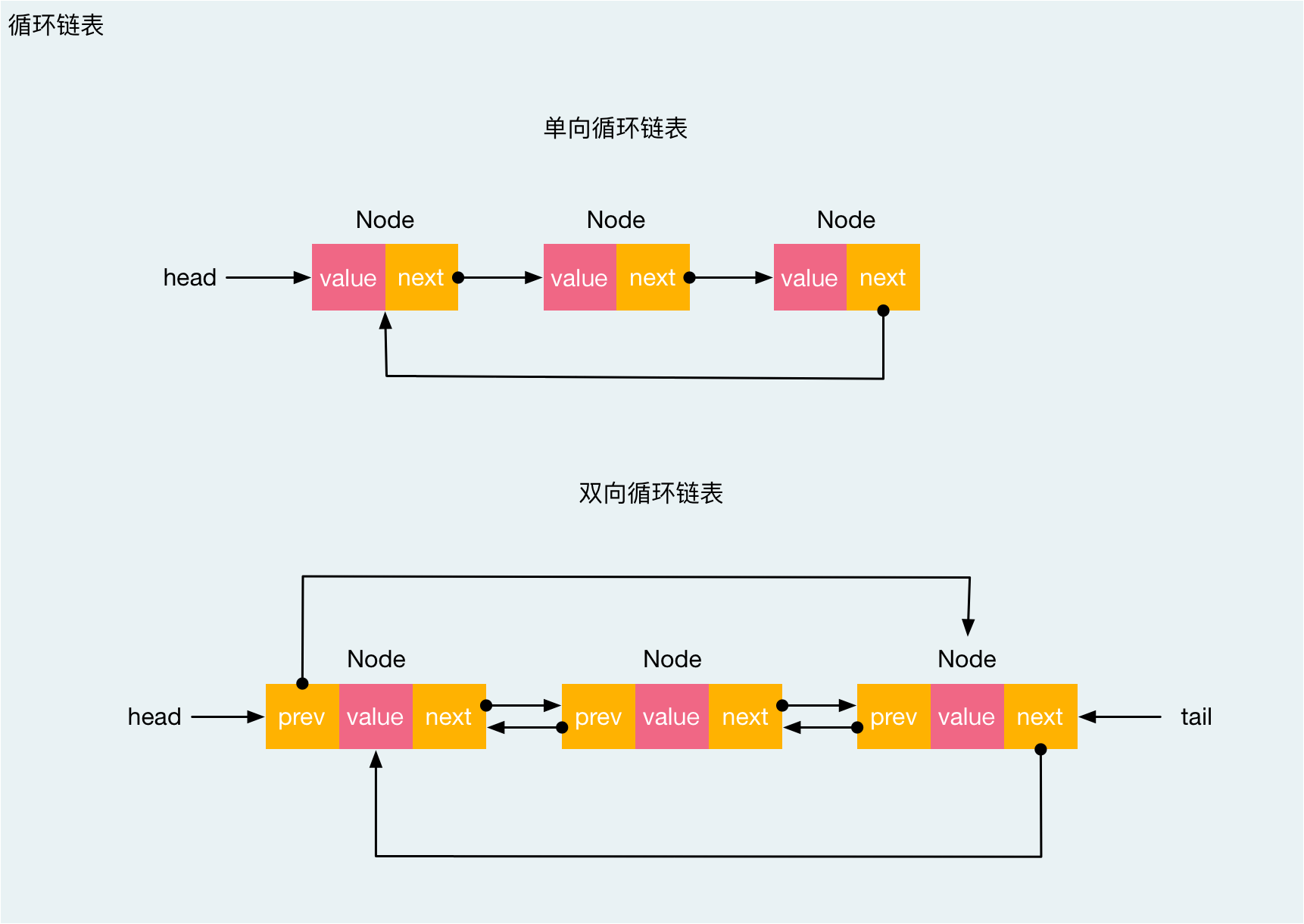
实现循环链表
CircularLinkedList 类不需要任何额外的属性,所以直接扩展 LinkedList 类并覆盖需要改写的方法即可。
class CircularLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals) {
super(equalsFn);
}
/**
* 添加元素
*/
push(element) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current;
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.getElementAt(this.size() - 1);
current.next = node;
}
// 把 node.next 指向 head,形成循环列表
node.next = this.head;
this.count++;
}
/**
* 在任意位置插入新元素
*/
insert(element, index) {
// 向循环链表中插入元素的逻辑和向普通链表中插入元素的逻辑是一样的
// 不同之处在于我们需要将循环链表尾部节点的 next 引用指向头部节点
if (index >= 0 && index <= this.count) {
const node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
//场景一:在循环链表第一个位置插入新元素
if (index === 0) {
if (this.head == null) {
// 链表为空
// 将 head 赋值为新创建的元素 node
this.head = node;
// 并且将最后一个节点链接到 head
node.next = this.head;
} else {
// 场景二:在一个非空循环链表的第一个位置插入元素
// 将 node.next 指向现在的 head 引用的节点(current 变量)
node.next = current;
// 获取取最后一个元素的引用
current = this.getElementAt(this.size());
// 头部元素更新为新元素,再将最后一个节点(current) 指向新的头部节点
this.head = node;
current.next = this.head;
}
} else {
// 场景三:在循环链表中间插入新元素
// 这种场景相对普通链表没有变化
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
node.next = previous.next;
previous.next = node;
}
this.count++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
*
*/
removeAt(index) {
if (index >= 0 && index < this.count) {
let current = this.head;
// 场景一:从只有一个元素的循环链表中移除一个元素
if (index === 0) {
if (this.size() === 1) {
this.head = null;
} else {
// 场景二:相对于普通链表只需要考虑第二种情况,也就是一个非空循环链表中移除第一个元素
// 即修改循环链表的 head 元素,由于 head 的指向会改变,需修改最后一个节点的 next 属性
// 1. 首先保存现在的 head 元素的引用,它将从循环链表中移除
const removed = this.head;
// 2. 获得循环链表最后一个元素��的引用
current = this.getElementAt(this.size() - 1);
// 3. 先更新 head 元素,将其指向第二个元素 head.next
this.head = this.head.next;
// 将最后一个元素(current.next)指向新的 head
current.next = this.head;
// 更新 current 变量的引用
current = removed;
}
} else {
// 不需要修改循环链表最后一个元素
const previous = this.getElementAt(index - 1);
current = previous.next;
previous.next = current.next;
}
this.count--;
return current.element;
}
return null;
}
}
有序链表
有序链表是指保持元素有序的链表结构。除了使用排序算法之外,我们还可以将元素插入到 正确的位置来保证链表的有序性。
实现有序链表
SortedLinkedList 类会从 LinkedList 类中继承所有的属性和方法,但由于这个类有特别的行为,我们需要一个用来比较元素的函数。因此,还需要声明 compareFn 函数来比较元素。该函数会默认使用 defaultCompare。如果元素有相同的引用,它就返回 0。如果第一个元素小于第二个元素,它就返回 -1,反之则返回 1。
为了保证代码优雅,我们可以声明一个 Compare 常量来表示每个值。如果用于比较的元素更复杂一些,我们可以创建自定义的 比较函数并将它传入 SortedLinkedList 类的构造函数中。
// 比较常量
const Compare = {
LESS_THAN: -1,
BIGGER_THAN: 1,
};
/**
* 比较函数
*/
function defaultCompare(a, b) {
if (a === b) {
return 0;
}
return a < b ? Compare.LESS_THAN : Compare.BIGGER_THAN;
}
/**
* 有序链表继承普通链表
*/
class SortedLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(equalsFn = defaultEquals, compareFn = defaultCompare) {
super(equalsFn);
this.equalsFn = equalsFn;
this.compareFn = compareFn;
}
/**
* 添加元素
*/
push(element) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
// 为空
super.push(element);
} else {
// 部位空,根据位置添加
const index = this.getIndexNextSortedElement(element);
super.insert(element, index);
}
}
/**
* 有序插入元素
* 由于不允许在任何位置插入元素,要给 index 参数设置一个默认值
* 直接调用 sortlist.insert(element)无须传入 index 参数
*/
insert(element, index = 0) {
// 如果 index 参数传入,它的值会被忽略,因为插入元素的位置是内部控制的
// 原因是不想重写整个 LinkedList 类的方法,我们只需要覆盖 insert 方法的行为。
if (this.isEmpty()) {
// 如果有序链表为空,直接调用 LinkedList 的 insert 方法并传入 0 作为 index
// return super.insert(element, 0);
return super.insert(element, index === 0 ? index : 0);
}
// 有序链表不为空,要获取插入元素的正确位置
const pos = this.getIndexNextSortedElement(element);
// 并根据位置并调用 LinkedList 的 insert 方法,传入该位置来保证链表有序
return super.insert(element, pos);
}
/**
* 获得插入元素的正确位置
*/
getIndexNextSortedElement(element) {
let current = this.head;
let i = 0;
// 迭代整个有序链表直至找到需要插入元素的位置
for (; i < this.size() && current; i++) {
// 使用 compareFn 来比较传入构造函数的元素
const comp = this.compareFn(element, current.element);
// 我们要插入有序链表 的元素小于 current 的元素时,我们就找到了插入元素的位置
if (comp === Compare.LESS_THAN) {
return i;
}
current = current.next;
}
// 或是迭代完所有的元素,返回的 index 将是有序链表的长度(元素将被插入在链表的末尾)
return i;
}
}
创建 StackLinkedList 类
LinkedList 类及其变种作为内部的数据结构来创建其他数据结构,例如栈、队列和双向队列。
使用双向链表实现栈数据结构:之所以使用双向链表而不是链表,是因为对栈来说,我们会向链表尾部添加元素,也会从链表尾部移除元素。DoublyLinkedList 类有列表最后一个元素(tail)的引用,无须迭代整个链表的元素就能获取它。双向链表可以直接获取头�尾的元素,减少过程消耗,它的时间复杂度和原始的 Stack 实现相同,为 O(1)。
也可以对 LinkedList 类进行优化,保存一个指向尾部元素的引用,并使用这个优化版本来代替 DoublyLinkedList。
class StackLinkedList {
constructor() {
// 将使用双向链表(DoublyLinkedList)来存储数据
this.items = new DoublyLinkedList();
}
push(element) {
this.items.push(element);
}
pop() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
const result = this.items.removeAt(this.size() - 1);
return result;
}
peek() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return undefined;
}
return this.items.getElementAt(this.size() - 1).element;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.items.isEmpty();
}
size() {
return this.items.size();
}
clear() {
this.items.clear();
}
toString() {
return this.items.toString();
}
}
相同的逻辑,可以使用 DoublyLinkedList 来创建 Queue 和 Deque 类,甚至使用 LinkedList 类也是可以的!