字典和散列表
字典
在计算机科学中,字典(Dictionary),又称映射(Map)、关联数组(Associative Array)是一个抽象的数据结构,它包含着类似于(键,值)的有序对,其中键名是用来查询特定元素的。
实现字典类
与 Set 类相似,ES6 同样包含了一个 Map 类的实现,即我们所说的字典。但不同于存储 [值,值] 对的形式,我们将要存储的是 [键,值] 对。
在字典中,理想的情况是用字符串作为键名,值可以是任何类型(从数、字符串等原始类型,到复杂的对象)。但是,由于 JavaScript 不是强类型的语言,我们需要把所有作为键名传入的对象转化为字符串,使得从 Dictionary 类中搜索和获取值更简单。所以需要一个将 key 转化为字符串的函数(toStrFn)。
需要声明一些映射/字典所能使用的方法:
set(key,value):向字典中添加新元素。如果key已经存在,那么已存在的value会 被新的值覆盖。remove(key):通过使用键值作为参数来从字典中移除键值对应的数据值。hasKey(key):如果某个键值存在于该字典中,返回true,否则返回false。get(key):通过以键值作为参数查找特定的数值并返回。clear():删除该字典中的所有值。size():返回字典所包含值的数量。与数组的length属性类似。isEmpty():在size等于零的时候返回true,否则返回false。keys():将字典所包含的所有键名以数组形式返回。values():将字典所包含的所有数值以数组形式返回。keyValues():将字典中所有[键,值]对返回。forEach(callbackFn):迭代字典中所有的键值对。callbackFn有两个参数:key和value。该方法可以在回调函数返回false时被中止(和 Array 类中的every方法相似)。
/**
* 转字符串,item 可选。用于转换字典 key
*/
function defaultToString(item) {
if (item === null) {
return 'null';
} else if (item === undefined) {
return 'undefined';
} else if (typeof item === 'string' || item instanceof String) {
return `${item}`;
}
// 如果为对象,调用它自身的 toString 方法
return item.toString();
}
/**
* 存储值信息的类
*/
class ValuePair {
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
toString() {
return `[#${this.key}: ${this.value}]`;
}
}
/**
* 字典类
*/
class Dictionary {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
// 转换 key 的函数
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
// 使用 Object 实例存储字典中的元素
// 保存为 table[key] = {key, value}
this.table = {};
}
/**
* 添加新的值,或者更新已有的值
*/
set(key, value) {
// 如果 key 和 value 不是 undefined 或 null,
if (key != null && value != null) {
// 那么我们获取表示 key 的字符串
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
// 实例化一个新的键值对并将其赋值给 table 对象上的 key 属性(tableKey)
this.table[tableKey] = new ValuePair(key, value);
// 返回 true
return true;
}
// 否则返回 false
return false;
}
/**
* 从字典中检索一个值
*/
get(key) {
// 首先会检索存储在给定 key 属性中的对象
const valuePair = this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
// 如果 valuePair 对象存在将返回该值,否则将返回一个 undefined 值
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
/**
* 检测一个键是否存在于字典中
*/
hasKey(key) {
// 根据给定键名的获取值
// 值不是 null 或 undefined 返回 true,否则返回 false
return this.table[this.toStrFn(key)] != null;
}
/**
* 从字典中移除一个值
*/
remove(key) {
// 存在值
if (this.hasKey(key)) {
// 使用 delete 运算符来从 items 对象中移除 key 属性
delete this.table[this.toStrFn(key)];
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 返回一个字典包含的所有值的数组
*/
values() {
return this.keyValues().map((valuePair) => valuePair.value);
}
/**
* 该方法返回字典类中用于识别值的所有(原始)键名的数组
*/
keys() {
return this.keyValues().map((valuePair) => valuePair.key);
}
/**
* 获取字典所有值的数组
*/
keyValues() {
// 以数组形式返回字典中的所有 valuePair 对象
return Object.values(this.table);
}
/**
* 迭代字典中的每个键值对
*/
forEach(callbackFn) {
// 获取字典中所有值构成的数组
const valuePairs = this.keyValues();
// 迭代每个值,并执行以参数形式传入回调函数 callbackFn
for (let i = 0; i < valuePairs.length; i++) {
const result = callbackFn(valuePairs[i].key, valuePairs[i].value);
// 如果回调函数返回了 false,中断迭代
if (result === false) {
break;
}
}
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const valuePairs = this.keyValues();
let objString = `${valuePairs[0].toString()}`;
for (let i = 1; i < valuePairs.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},${valuePairs[i].toString()}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
测试 Dictionary 类:
const dictionary = new Dictionary();
dictionary.set('one', '一');
dictionary.set('two', '二');
console.log(dictionary.hasKey('one')); // 输出 true
console.log(dictionary.size()); // 输出 2
console.log(dictionary.keys()); // 输出 ["one", "two"]
console.log(dictionary.values()); // 输出 ["一", "二"]
console.log(dictionary.get('two')); // 输出 “二”
dictionary.forEach((k, v) => {
console.log('forEach: ', `key: ${k}, value: ${v}`);
});
// forEach: key: "one", value: "一"
// forEach: key: "two", value: "二"
散列表
散列表(Hash Table,也叫哈希表),是根据键(Key)而直接访问在内存储存位置的数据结构。也就是说,它通过计算一个关于键值的函数,将所需查询的数据映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,这加快了查找速度。这个映射函数称做散列函数,存放记录的数组称做散列表。
散列表有一些在计算机科学中应用的例子。因为它是字典的一种实现,所以可以用作关联数 组。它也可以用来对数据库进行索引。当我们在关系型数据库(如 MySQL、Microsoft SQL Server、 Oracle,等等)中创建一个新的表时,一个不错的做法是同时创建一个索引来更快地查询到记录 的 key。在这种情况下,散列表可以用来保存键和对表中记录的引用。另一个很常见的应用是使 用散列表来表示对象。JavaScript 语言内部就是使用散列表来表示每个对象。此时,对象的每个 属性和方法(成员)被存储为 key 对象类型,每个 key 指向对应的对象成员。
以字典测试的中文数字为例。我们将使用最常见的散列函数——lose lose 散列函数,方法是简单地将每个键值中的每个字母的 ASCII 值相加,如下所示:
| 名称/键 | 散列函数 | 散列值 | 散列表 |
|---|---|---|---|
| "one" | 111+110+101 | 322 | [322] => ["一"] |
| "two" | 116+119+111 | 346 | [346] => ["二"] |
| "three" | 116+104+114+114 | 448 | [448] => ["三"] |
了解更多关于 ASCII 的信息,访问 http://www.asciitable.com
实现散列表
给类实现三个基本方法:
put(key,value):向散列表增加一个新的项(也能更新散列表)。remove(key):根据键值从散列表中移除值。get(key):返回根据键值检索到的特定的值
/**
* 散列/哈希表
*/
class HashTable {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
/**
* 创建散列函数
* 给定一个 key 参数,根据组成 key 的每个字符的 ASCII 码值的和得到一个数
*/
loseloseHashCode(key) {
// 首先检验 key 是否是一个数
if (typeof key === 'number') {
// 是,直接将其返回
return key;
}
// 将 key 转换为一个字符串
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
// 定义 hash 变量来存储这个总和
let hash = 0;
// 遍历 key 并将从 ASCII 表中查到的每个字符对应的 ASCII 值加到 hash 变量中
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
// 使用 String 类中的 charCodeAt 方法转换 ASCII 值
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
// 使用 hash 值 和一个任意数做除法的余数(%)
// 这可以规避操作数超过数值变量最大表示范围的风险
return hash % 37;
}
/**
* 调用了 loseloseHashCode 方法,将 key 作为参数传入
*/
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
/**
* 将键和值加入散列表
*/
put(key, value) {
// 检验 key 和 value 是否合法
if (key != null && value != null) {
// 用 hashCode 函数在表中找到一个位置
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 用 key 和 value 创建一个 ValuePair 实例
this.table[position] = new ValuePair(key, value);
return true;
}
// 不合法返回 false,表示值没有被添加(更新)
return false;
}
/**
* 从散列表中获取一个值
*/
get(key) {
// 返回对应值的位置,取对应位置的值并返回
const valuePair = this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
/**
* 从散列表中移除一个值
*/
remove(key) {
// 首先需要知道值所在的位置,因此使用 hashCode 函数来获取 hash
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
// 在 hash 的位置获取到 valuePair
const valuePair = this.table[hash];
// 如果值 valuePair 不是 null 或 undefined
if (valuePair != null) {
// 就使用 delete 运算符将其删除
// [还可以将删除的 hash 位置赋值为 null 或 undefined]
delete this.table[hash];
// 如果删除成功,就返回 true
return true;
}
// 否则返回 false
return false;
}
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[keys[i]].toString()}}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
测试散列/哈希表:
const hash = new HashTable();
hash.put('one', '一');
hash.put('two', '二');
hash.put('three', '三');
console.log(hash.hashCode('one')); // 输出 26
console.log(hash.get('one')); // 输出 一
散列表和散列集合
散列集合由一个集合构成,但是插入、移除或获取元素时,使用的是 hashCode 函数。复用哈希表实现的所有代码来实现散列 集合,不同之处在于,不再添加键值对,而是只插入值而没有键。例如,可以使用散列集合来存 储所有的英语单词(不包括它们的定义)。和集合相似,散列集合只存储不重复的唯一值。
处理散列表中的冲突
有时候,一些键会有相同的散列值。不同的值在散列表中对应相同位置的时候,我们称其为冲突。处理冲突有几种方法:分离链接、线性探查和双散列法
解决冲突的方法:
- 开放定址法
- 单独链表法(链地址法/拉链法/分离链接):将散列到同一个存储位置的所有元素保存在一个链表中。
- 再散列法
- 双散列法
- 建立一个公共溢出区
分离链接
分离链接法包括为散列表的每一个位置创建一个链表并将元素存储在里面。它是解决冲突的最简单的方法,但是在 HashTable 实例之外还需要额外的存储空间。
比如有通过 HashTable 的 toString 方法打印出来散列表中存储的信息:
{4 => [#Ygritte: ygritte@email.com]}
{5 => [#Aethelwulf: aethelwulf@email.com]}
{7 => [#Athelstan: athelstan@email.com]}
{8 => [#Jasmine: jasmine@email.com]}
{9 => [#Jake: jake@email.com]}
{10 => [#Sargeras: sargeras@email.com]}
使用分离链接并用�图表示的话,输出结果将会是如下这样(为了简化,图表中的值被省略了):
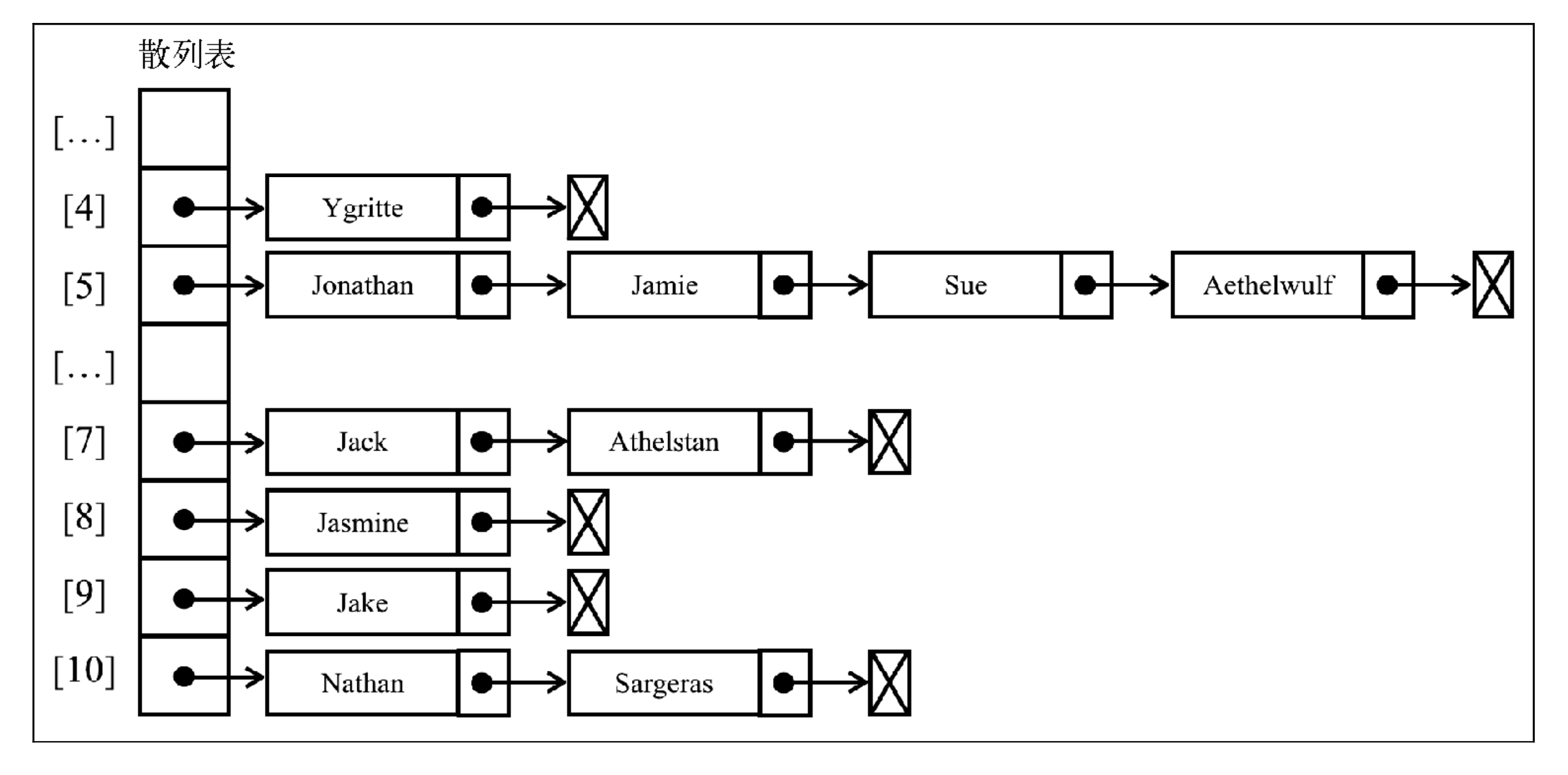
在位置 5 上,将会有包含四个元素的 LinkedList 实例;在位置 7 和 10 上,将会有包含两 个元素的 LinkedList 实例;在位置 4、8 和 9 上,将会有包含单个元素的 LinkedList 实例。
线性探查
另一种解决冲突的方法是线性探查。之所以称作线性,是因为它处理冲突的方法是将元素直接存储到表中,而不是在单独的数据结构中。
当想向表中某个位置添加一个新元素的时候,如果索引为 position 的位置已经被占据了,就尝试 position+1 的位置。如果 position+1 的位置也被占据了,就尝试 position+2 的位置,以此类推,直到在散列表中找到一个空闲的位置。
想象一下,有一个已经包含一些元素的散列表,我们想要添加一个新的键和值。我们计算这个新键的 hash,并检查散列表中对应的位置是否被占据。如果没有,我们就将该值添加到正确的位置。如果被占据了,我们就迭代散列表,直到找到一个空闲的位置。
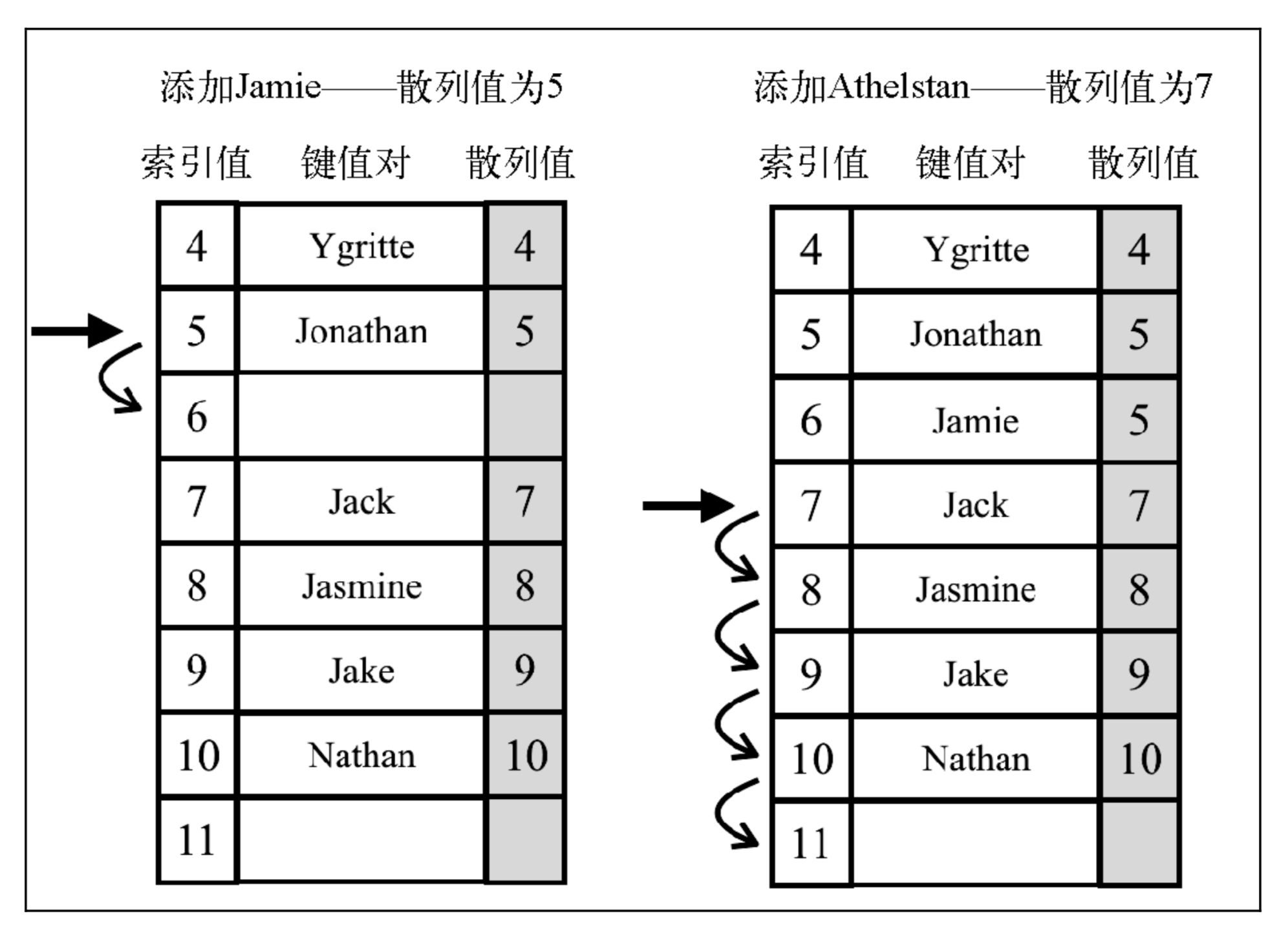
当我们从散列表中移除一个键值对的时候,之前的数据结构所实现位置的元素移除是不够的。如果我们只是移除了元素,就可能在查找有相同 hash(位置)的其他元素时找到一个空的位置�,这会导致算法出现问题。
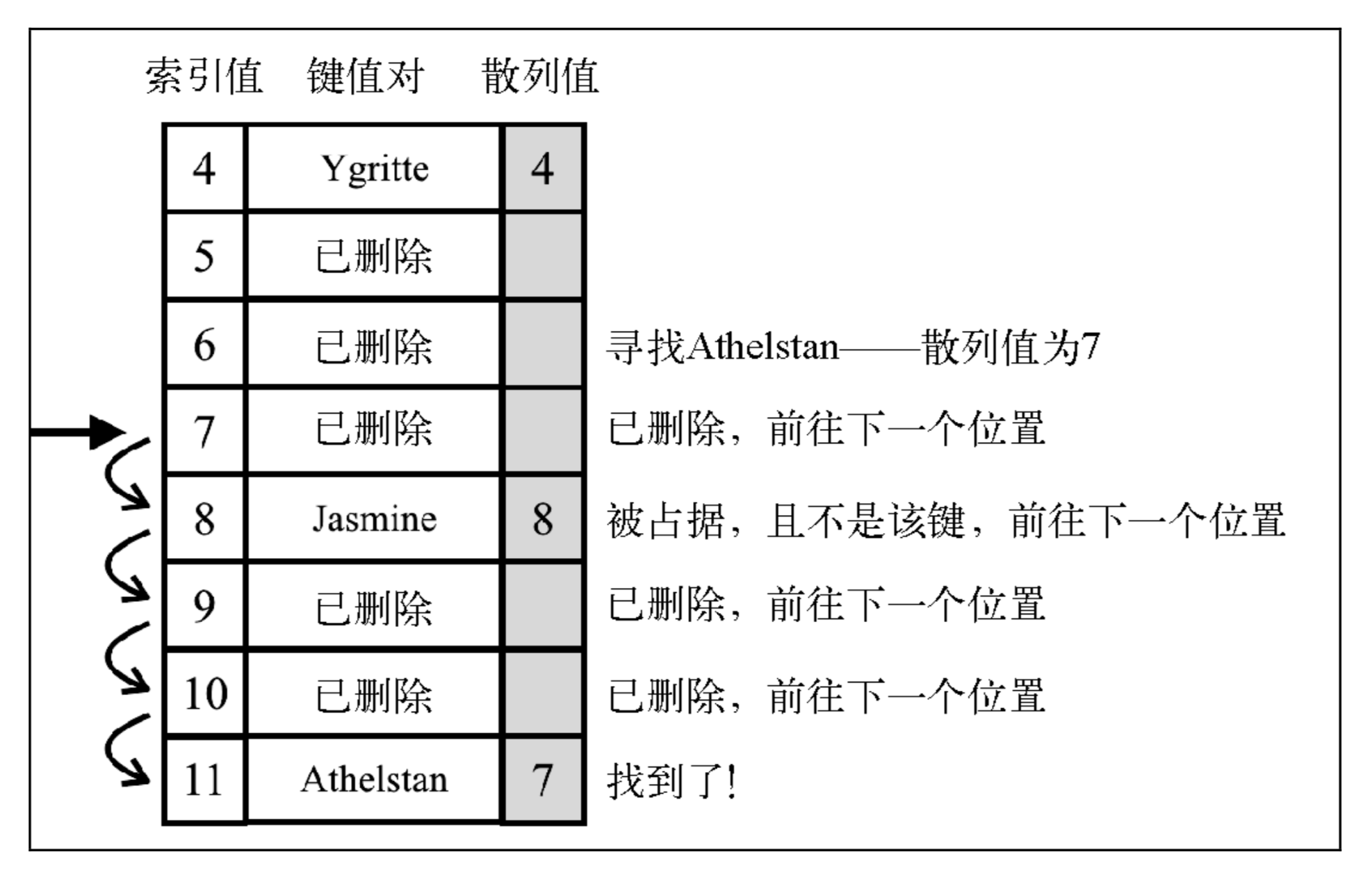
线性探查技术分为两种。第一种是软删除方法。我们使用一个特殊的值(标记)来表示键值对被删除了(惰性删除或软删除),而不是真的删除它。经过一段时间,散列表被操作过后,我们会得到一个标记了若干删除位置的散列表。这会逐渐降低散列表的效率,因为搜索键值会随时间变得更慢。能快速访问并找到一个键是我们使用散列表的一个重要原因。下图展示了这个过程:
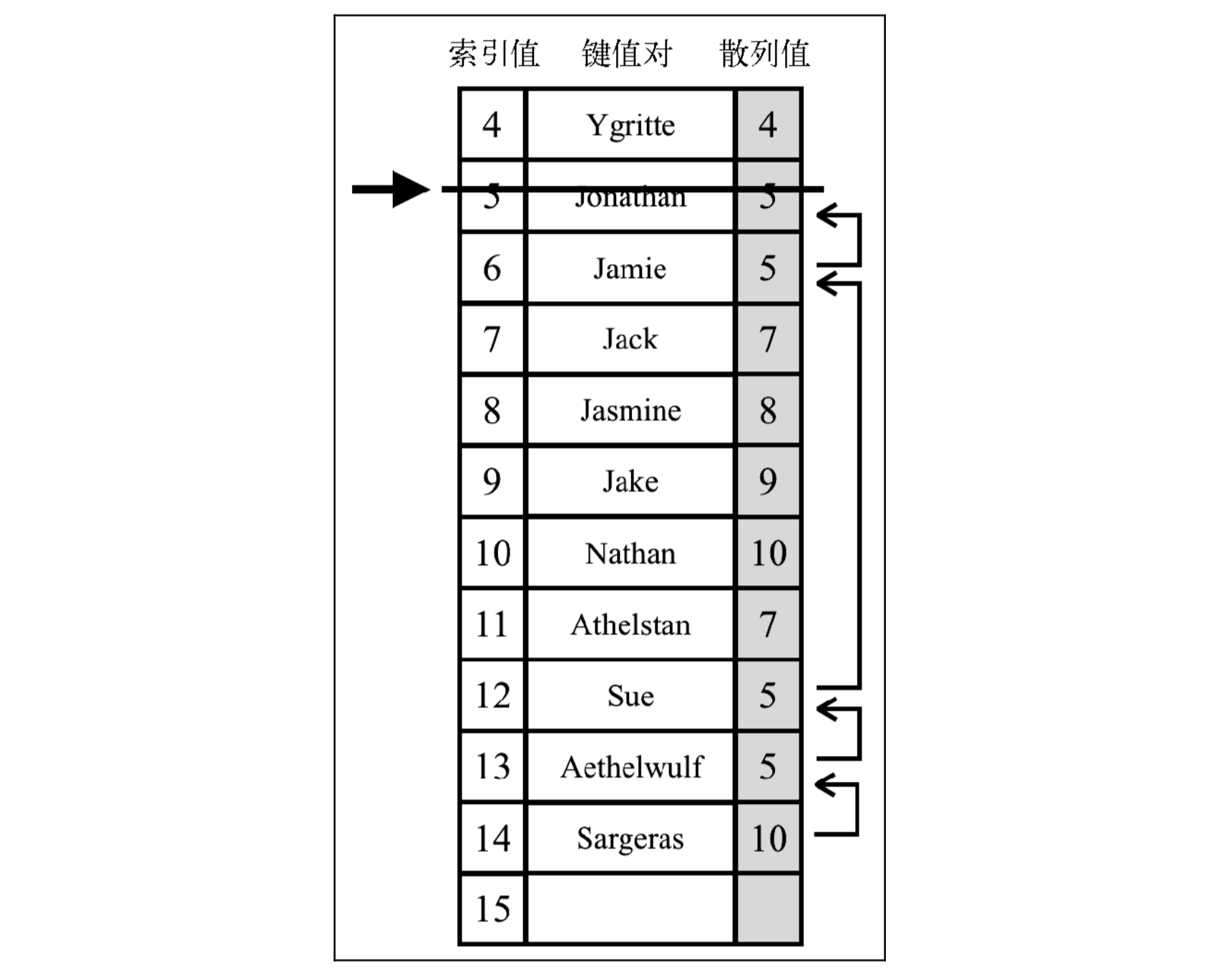
第二种方法需要检验是否有必要将一个或多个元素移动到之前的位置。当搜索一个键的时候,这种方法可以避免找到一个空位置。如果移动元素是必要的,我们就需要在散列表中挪动键 6 值对。下图展现了这个过程:
实现分离链接和线性探查
对于分离链接和线性探查来说,只需要重写三个方法:put、get 和 remove。这三个方法 在每种技术实现中都是不同的。提前公共方法 defaultToString,ValuePair 并导入链表类 LinkedList。
- 分离链接
- 线性探查
- 线性探查(惰性删除)
// 提取上面定义的方法为公共方法
import { defaultToString } from '../util';
import LinkedList from './linked-list';
import { ValuePair } from './models/value-pair';
/* 散列表:使用分离链接法来处理冲突的 HashTable - SeparateChaining 类 */
class HashTableSeparateChaining {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
loseloseHashCode(key) {
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37;
}
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
/**
* 加入新元素到散列表中
*/
put(key, value) {
// 校验合法性
if (key != null && value != null) {
// 验证要加入新元素的位置是否已经被占据
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[position] == null) {
// 如果是第一次向该位置加入元素,在该位置上初始化一个 LinkedList 类的实例
this.table[position] = new LinkedList();
}
// 向 LinkedList 实例中添加一个 ValuePair 实例(键和值)
this.table[position].push(new ValuePair(key, value));
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 从散列表中获取给定键的值
*/
get(key) {
// 验证的是在特定的位置上是否有元素存在
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 在 position 位置检索 linkedList
const linkedList = this.table[position];
// 并检验是否存在 linkedList 实例
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
// 如果该位置上有值存在,我们知道这是一个 LinkedList 实例
// 要做的是迭代这个链表来寻找我们需要的元素
// 在迭代之前先要获取链 表表头的引用
let current = linkedList.getHead();
// 然后就可以从链表的头部迭代到尾部(最后 current.next 将会是 null)
while (current != null) {
// Node 链表包含 next 指针和 element 属性。而 element 属性�又是 ValuePair 的实例
// 所以 element 有 value 和 key 属性,可以通过 current.element.key 来获得 Node 链表的 key 属性
// 并通过比较 key 来确定它是否就是我们要找的键(key)
if (current.element.key === key) {
// 如果 key 值相同,就返回 Node 的值(value)
return current.element.value;
}
// 如果 key 不相同,就继续迭代链表,访问下一个节点
current = current.next;
}
}
// 如果没有 linkedList 实例,则返回一个 undefined
// 表示在 HashTable 实例中没有找到这个值
return undefined;
}
/**
* 从散列表中移除一个元素
*/
remove(key) {
// 和 get 方法相同,先要找到要移除的元素
const position = this.hashCode(key);
const linkedList = this.table[position];
if (linkedList != null && !linkedList.isEmpty()) {
let current = linkedList.getHead();
while (current != null) {
// 迭代 LinkedList 实例时,如果链表中的 current 元素就是要找的元素
if (current.element.key === key) {
// 使用 remove 方法将其从链表中移除
linkedList.remove(current.element);
// 然后进行一步额外的验证:如果链表为空了,就使用 delete 运算符将散列表的该位置删除
// 这样搜索一个元素的时候,就可以跳过这个位置了
if (linkedList.isEmpty()) {
delete this.table[position];
}
// 返回 true 表示该元素已经被移除
return true;
}
// 继续迭代链表,访问下一个节点
current = current.next;
}
}
// 在最后返回 false 表示该元素在散列表中不存在
return false;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
let count = 0;
Object.values(this.table).forEach((linkedList) => {
count += linkedList.size();
});
return count;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[keys[i]].toString()}}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
import { defaultToString } from '../util';
import { ValuePairLazy } from './models/value-pair-lazy';
/**
* 散列表:线性探查,删除后移动位置
*/
class HashTableLinearProbing {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
loseloseHashCode(key) {
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37;
}
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
/**
* 添加新元素到散列表中
*/
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
// 获得由散列函数生成的位置
const position = this.hashCode(key);
// 然后验证这个位置是否有元素存在
if (this.table[position] == null) {
// 如果没有元素存在(这是最简单的场景),就在这个位置添加新元素(ValuePair 的实例)
this.table[position] = new ValuePair(key, value);
} else {
// 如果该位置已经被占据了,需要找到下一个没有被占据的位置(position 的值是 undefined 或 null)
// 因此我们声明一个 index 变量并赋值为 position+1
let index = position + 1;
// 然后验证该位置是否被占据
while (this.table[index] != null) {
// 如果被占据了,继续将 index 递增直到找到一个没有被占据的位置
index++;
}
// 找到一个没有被占据的位置,然后就是将值分配到该位置
this.table[index] = new ValuePair(key, value);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 从散列表中获得一个键对应的值
*/
get(key) {
// 先要确定这个键存在
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[position] != null) {
// 如果这个键存在,需要检查我们要找的值是否就是原始位置上的值
if (this.table[position].key === key) {
// 如果是原始位置上,就返回这个值
return this.table[position].value;
}
// 如果不是在原始位置,就在 HashTableLinearProbing 的下一个位置继续查找
let index = position + 1;
// 按位置递增的顺序查找散列表上的元素直到找到我们要找的元素,或者找到一个空位置
while (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key !== key) {
index++;
}
// 当从 while 循环跳出的时候,要验证元素的键是否是我们要找的键
if (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key === key) {
// 如果是元素的键是要找的键,就返回它的值
return this.table[position].value;
}
}
// 如果这个键不存在,说明要查找的值不在散列表中,可以返回 undefined
// 或者迭代完整个散列表并且 index 的位置上是 undefined 或 null 的话,说明要找的键不存在
return undefined;
}
/**
* 从散列表中删除元素
*/
remove(key) {
// remove 方法和 get 方法基本相同
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[position] != null) {
if (this.table[position].key === key) {
// 从原始 hash 位置找到元素,直接删除
delete this.table[position];
// 由于我们不知道在散列表的不同位置上是否存在具有相同 hash 的元素,需要验证删除操作是否有副作用
// 如果有,就需要将冲突的元素移动至一个之前的位置,这样就不会产生空位置。
this.verifyRemoveSideEffect(key, position);
return true;
}
let index = position + 1;
while (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key !== key) {
index++;
}
if (this.table[index] != null && this.table[index].key === key) {
// 如果有冲突并被处理了,可以在另一个位置找到元素
delete this.table[index];
// 同上
this.verifyRemoveSideEffect(key, index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 方法接收两个参数:被删除的 key 和该 key 被删除的位置
*/
verifyRemoveSideEffect(key, removedPosition) {
// 我们要获取被删除的 key 的 hash 值(也可以将该值作为一个参数传入这个方法)
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
// 然后,从下一个位置开始迭代散列表,直到找到一个空位置
let index = removedPosition + 1;
while (this.table[index] != null) {
// 当空位置被找到后,表示元素都在合适的位置上,不需要进行移动(或更多的移动)
// 当迭代随后的元素时,我们需要计算当前位置上元素的 hash 值
const posHash = this.hashCode(this.table[index].key);
// 如果当前元素的 hash 值小于或等于原始的 hash 值
// 或者当前元素的 hash 值小于或等于 removedPosition(也就是上一个被移除 key 的 hash 值)
if (posHash <= hash || posHash <= removedPosition) {
// 表示我们需要将当前元素移动至 removedPosition 的位置
this.table[removedPosition] = this.table[index];
// 移动完成后,我们可以删除当前的元素(因为它已经被复制到 removedPosition 的位 置了)
delete this.table[index];
// 还需要将 removedPosition 更新为当前的 index,然后重复这个过程
removedPosition = index;
}
index++;
}
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[keys[i]].toString()}}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
import { defaultToString } from '../util';
// import { ValuePairLazy } from './models/value-pair-lazy';
class ValuePairLazy extends ValuePair {
constructor(key, value, isDeleted = false) {
super(key, value);
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.isDeleted = isDeleted;
}
}
/**
* 散列表:线性探查(软/惰性删除)
*/
class HashTableLinearProbingLazy {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
loseloseHashCode(key) {
if (typeof key === 'number') {
return key;
}
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash += tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 37;
}
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (
this.table[position] == null ||
(this.table[position] != null && this.table[position].isDeleted)
) {
this.table[position] = new ValuePairLazy(key, value);
} else {
let index = position + 1;
while (this.table[index] != null && !this.table[position].isDeleted) {
index++;
}
this.table[index] = new ValuePairLazy(key, value);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[position] != null) {
if (this.table[position].key === key && !this.table[position].isDeleted) {
return this.table[position].value;
}
let index = position + 1;
while (
this.table[index] != null &&
(this.table[index].key !== key || this.table[index].isDeleted)
) {
if (this.table[index].key === key && this.table[index].isDeleted) {
return undefined;
}
index++;
}
if (
this.table[index] != null &&
this.table[index].key === key &&
!this.table[index].isDeleted
) {
return this.table[position].value;
}
}
return undefined;
}
remove(key) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
if (this.table[position] != null) {
if (this.table[position].key === key && !this.table[position].isDeleted) {
this.table[position].isDeleted = true;
return true;
}
let index = position + 1;
while (
this.table[index] != null &&
(this.table[index].key !== key || this.table[index].isDeleted)
) {
index++;
}
if (
this.table[index] != null &&
this.table[index].key === key &&
!this.table[index].isDeleted
) {
this.table[index].isDeleted = true;
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
let count = 0;
Object.values(this.table).forEach((valuePair) => {
count += valuePair.isDeleted === true ? 0 : 1;
});
return count;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[keys[i]].toString()}}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
创建更好的散列函数
lose lose 散列函数并不是一个表现良好的散列函数,因为它会产生太多的冲突。一个表现良好的散列函数是由几个方面构成的:插入和检索元素的时间(即性能),以及较低的 冲突可能性。可以在网上找到一些不同的实现方法,也可以实现自己的散列函数。
另一个可以实现的、比 lose lose 更好的散列函数是 djb2
- djb2HashCode 函数
- 完整 HashTable 类
/**
* lose lose 更好的散列函数是 djb2
*/
djb2HashCode(key) {
// 将键转化为字符串之后
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
// 初始化一个 hash 变量并赋值 为一个质数(大多数实现都使用 5381)
let hash = 5381;
// 迭代参数 key
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
// 将 hash 与 33 相乘(用作一个幻数),并和当前迭代到的字符的 ASCII 码值相加
hash = (hash * 33) + tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
// 将使用相加的和与另一个随机质数相除的余数,比我们认为的散列表大小要大。比如认为散列表的大小为 1000
return hash % 1013;
}
// 使用上面提取的公共方法
import { defaultToString } from '../util';
import { ValuePair } from './models/value-pair';
class HashTable {
constructor(toStrFn = defaultToString) {
this.toStrFn = toStrFn;
this.table = {};
}
djb2HashCode(key) {
const tableKey = this.toStrFn(key);
let hash = 5381;
for (let i = 0; i < tableKey.length; i++) {
hash = hash * 33 + tableKey.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % 1013;
}
hashCode(key) {
return this.loseloseHashCode(key);
}
put(key, value) {
if (key != null && value != null) {
const position = this.hashCode(key);
this.table[position] = new ValuePair(key, value);
return true;
}
return false;
}
get(key) {
const valuePair = this.table[this.hashCode(key)];
return valuePair == null ? undefined : valuePair.value;
}
remove(key) {
const hash = this.hashCode(key);
const valuePair = this.table[hash];
if (valuePair != null) {
delete this.table[hash];
return true;
}
return false;
}
getTable() {
return this.table;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.size() === 0;
}
size() {
return Object.keys(this.table).length;
}
clear() {
this.table = {};
}
toString() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
return '';
}
const keys = Object.keys(this.table);
let objString = `{${keys[0]} => ${this.table[keys[0]].toString()}}`;
for (let i = 1; i < keys.length; i++) {
objString = `${objString},{${keys[i]} => ${this.table[keys[i]].toString()}}`;
}
return objString;
}
}
幻数在编程中指直接使用的常数。
构建散列函数的方法:
-
直接定址法:取关键字或关键字的某个线性函数值为散列地址。
-
数字分析法:分析一组数据,比如一组员工的出生年月日,这时我们发现出生年月日的前几位数字大体相同,这样的话,出现冲突的几率就会很大,但是我们发现年月日的后几位表示月份和具体日期的数字差别很大,如果用后面的数字来构成散列地址,则冲突的几率会明显降低。因此数字分析法就是找出数字的规律,尽可能利用这些数据来构造冲突几率较低的散列地址。
-
平方取中法:当无法确定关键字中哪几位分布较均匀时,可以先求出关键字的平方值,然后按需�要取平方值的中间几位作为哈希地址。这是因为:平方后中间几位和关键字中每一位都相关,故不同关键字会以较高的概率产生不同的哈希地址。
-
折叠法:将关键字分割成位数相同的几部分,最后一部分位数可以不同,然后取这几部分的叠加和(去除进位)作为散列地址。数位叠加可以有移位叠加和间界叠加两种方法。移位叠加是将分割后的每一部分的最低位对齐,然后相加;间界叠加是从一端向另一端沿分割界来回折叠,然后对齐相加。
-
随机数法:选择一随机函数,取关键字的随机值作为散列地址,即
H(key)=random(key)其中 random 为随机函数,通常用于关键字长度不等的场合。 -
除留余数法:取关键字被某个不大于散列表表长 m 的数 p 除后所得的余数为散列地址。即
H(key) = key MOD p,p<=m。不仅可以对关键字直接取模,也可在折叠、平方取中等运算之后取模。对 p 的选择很重要,一般取素数或 m,若 p 选的不好,容易产生同义词。
ES6 Map 类
ES6 中新增了 Map 类,可以基于 ES6 的 Map 类开发我们的字典(Dictionary)类。
和 Dictionary 类不同,ES2015 的 Map 类的 values 方法和 keys 方法都返回 Iterator,而不是值或键构成的数组。另一个区别是,我们实现的 size 方法 返回字典中存储的值的个数,而 ES2015 的 Map 类则有一个 size 属性。
关于 Map 类的实现细节,请查阅 ECMAScript 6 入门 和 MDN
ES6 WeakMap 类和 WeakSet 类
除了 Set 和 Map 这两种新的数据结构,ES2015 还增加了它们的弱化版本,WeakSet 和 WeakMap。
基本上 Map 和 Set 与其弱化版本之间仅有的区别是:
- WeakSet 或 WeakMap 类没有
entries、keys和values等方法 - 只能用对象作为键。
创建和使用这两个类主要是为了性能。WeakSet 和 WeakMap 是弱化的(用对象作为键),没有强引用的键。这使得 JavaScript 的垃圾回收器可以从中清除整个入口。
另一个优点是,必须用键才可以取出值。这些类没有 entries、keys 和 values 等迭代器方法,因此,除非你知道键,否则没有办法取出值。
了解更多,查阅 MDN WeakMap、MDN WeakSet 及 ECMAScript 6 入门